Spring03学习日记:AOP 面向切面编程
简单来说,是操作过程的复用。
前言
在面向对象(OOP)的时代。很多人在日常开发中会发现有些东西不像一个对象,其实是一个流程。
假设有这么一个流程1:对一个数据库发送请求-》拿数据1-》拿数据2-》展示数据
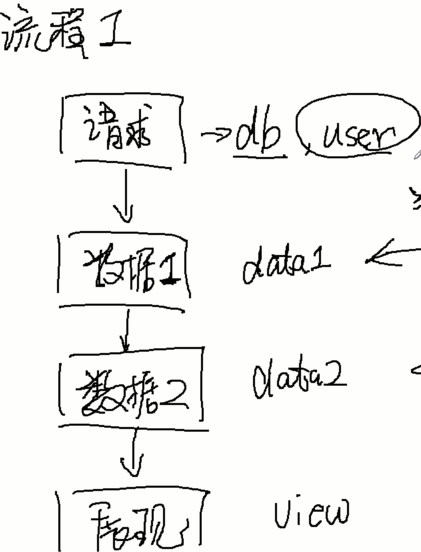
假设又有一个流程2,步骤比流程1多了一个步骤:
对一个数据库发送请求-》要求判断权限 -》拿数据1-》拿数据2-》展示数据
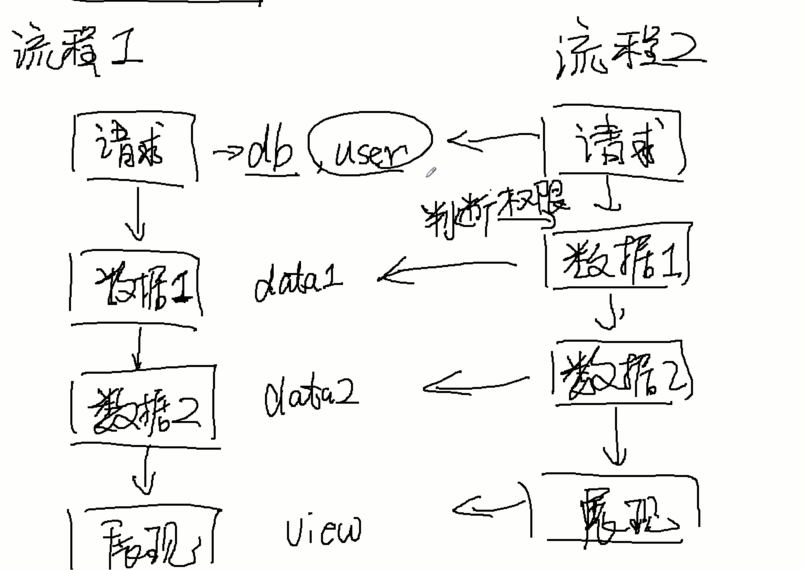
这种情况下,抽象这种流程是很难的,如果是用继承实现会有很大的耦合性,这个时候就要用到面向切面编程了。这种情况下就要使用代理了。
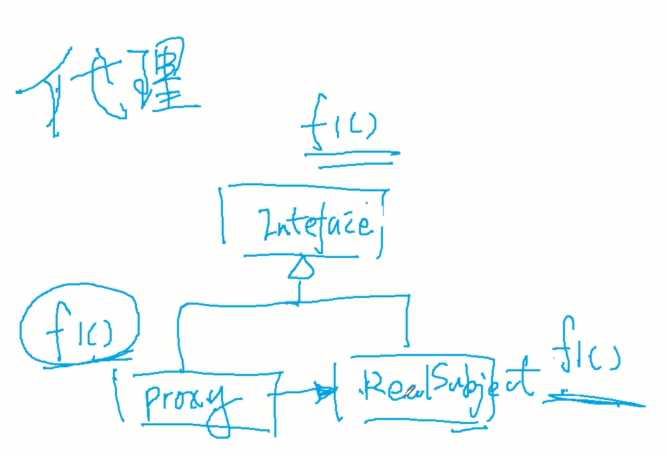
关于代理模式(静态代理、动态代理),以后专门拿出来写。。。
通过代理Proxy类对RealSubject类方法的调用,也可以添加属于代理类自己的一些代码(例如检查权限)
然后上面流程根据实际需求来决定是调用Proxy还是RealSubject去JointPoint
实际上,切面就有点像一个流程的类,JointPoint有点像流程的方法,然后通过动态代理的模式实现流程代码的复用。
一个简单的例子
根据前言所举得例子,进行代码的实现,使得概念了解的更加明白。
先用OOP举例,比如实现一个流程process,里面有三个步骤action1、action2、action3
public class process extends AbstractProcess{
// 步骤1
public void action1(){
System.out.println("action 1");
}
// 步骤2.
public void action2(){
System.out.println("action 2");
System.out.println("action 2 again");
}
// 步骤3.
public void action3(){
System.out.println("action 3");
}
}
这时候假如说又要开发一个流程process2,里面有的action2要在action1的基础上增加一些东西,使用OOP的话,如果以后再次增加新的流程process3、process4、….,我们很难将这些四处分散的代码模块化。
因此用代理模式比较可行。将proces作为RealSubject,利用Proxy模式去实现流程2、流程3等等。。代码如下:
先创建一个接口IProcess:
public interface IProcess {
void action1();
void action2();
void action3();
}
创建一个抽象类AbstractProcess实现IProcess
public abstract class AbstractProcess implements IProcess{
private IProcess process; // 实现类
public IProcess getProcess() {
return process;
}
public void setProcess(IProcess process) {
this.process = process;
}
public static void doActions(IProcess process) {
// 步骤1.
process.action1();
// 步骤2.
process.action2();
// 步骤3.
process.action3();
}
}
创建动态代理调用类
public class Process2InvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
private IProcess process;
public IProcess getProcess() {
return process;
}
public void setProcess(IProcess process) {
this.process = process;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Object returnValue = null;
// 通过调用的名称来判断
if ("action2".equals(method.getName())) {
System.out.println("before action 2");
returnValue = method.invoke(this.process, args);
System.out.println("after action 2");
} else {
returnValue = method.invoke(this.process, args);
}
return returnValue;
}
}
实现Process2
public static void main( String[] args )
{
Process2InvocationHandler handler = new Process2InvocationHandler();
handler.setProcess(process);
IProcess process2 = (IProcess) Proxy.newProxyInstance(process.getClass().getClassLoader(),
AbstractProcess.class.getInterfaces(),
handler);
}
概念
JoinPoint:那些可以切分开的一个一个的动作或者步骤
PointCut:那些我们企图劫持的JoinPoint(例如例子中的Process2动态代理对action1进行劫持)
Advice:当劫持了一个PointCut后,需要提前或者后置的动作,这个动作通常是调用一个回调函数,这个动作是Advice。
- 前置通知(在action以前通知)
- 后置通知(在action以后通知)
- 异常通知(类似于try … catch)
- 最终通知(类似于finally)
- 环绕通知(自己设置如何通知)
Introduction:通过反射实现的动态代理来实现Advice功能的过程
Proxy
Target:被代理的对象,真正干活的对象
Weaving:代理对象被创建的过程
Spring:反射实现动态代理(这里不介绍)
Spring + AspectJ (一个支持AOP的框架) :在编译时织入,在类装载时织入
Aspect:切面=PointCut + Advice
Spring AOP+AspectJ
maven依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.11</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!--spring依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-expression</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--spring aop依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--spring test-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--AspectJ-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.6</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
配置文件方式配置AOP
新建一个切面类Logger,以便观察
public class Logger {
public void printLog(){
System.out.println("Logger say xxx here!");
}
public Object processAdvice(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp){ // 环绕通知配置方式
System.out.println("Logger before action.");
Object rtValue = null;
try {
Object[] args = pjp.getArgs();
rtValue = pjp.proceed(args);
System.out.println("Logger after-returning action");
} catch (Throwable e) {
System.out.println("Logger after-throwing action");
} finally {
System.out.println("Logger after action");
}
return rtValue;
}
}
配置文件命名为bean.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!-- Target => proxy -->
<bean id="process" class="cn.silvercorridors.Process"></bean>
<!-- Logger -->
<bean id="logger" class="cn.silvercorridors.Logger"></bean>
<!-- AspectJ 直接修改process,使他变成一个proxy -->
<!--
pointcut = " execution(<方法表达式>) "
<方法表达式>:public void cn.silvercorridors.Process.action2()
-->
<aop:config>
<!-- 设定Aspect -->
<aop:aspect id="logAdvice" ref="logger"><!-- ref表示通知的类 -->
<aop:before method="printLog" pointcut="execution(public void cn.silvercorridors.Process.action2())"></aop:before><!--pointCut为要拦截的方法-->
<aop:after method="printLog" pointcut="execution(public void cn.silvercorridors.Process.action2())"></aop:after>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
运行函数
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
IProcess process = (IProcess) ac.getBean("process");
Process.doActions(process);
注解方式配置AOP
新建一个配置文件类
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "cn.qyx")
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class SpringConfiguration {
}
新建切面类Logger,以便观察,首先给Process与Logger加上与相应的component注解,然后直接在切面类中给相应的方法加注解
@Component("process")
@Component("logger")
切面类
@Component("logger")
public class Logger {
//@Around("action2()")//环绕
public Object processAdvice(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp){
System.out.println("Logger before action.");
Object rtValue = null;
try {
Object[] args = pjp.getArgs();
rtValue = pjp.proceed(args);
System.out.println("Logger after-returning action");
} catch (Throwable e) {
System.out.println("Logger after-throwing action");
} finally {
System.out.println("Logger after action");
}
return rtValue;
}
@Pointcut("execution(void cn.silvercorridors.Process.action2())")
private void action2(){};
@Before("action2()")
public void printBefore(){
System.out.println("Logger say Before here!");
}
@AfterReturning("action2()")
public void printAfterReturn(){
System.out.println("Logger say after return here!");
}
@AfterThrowing("action2()")
public void printAfterThrowing(){
System.out.println("Logger say after throwing here!");
}
@After("action2()")
public void printAfter(){
System.out.println("Logger say after here!");
}
运行函数
ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfiguration.class);
IProcess process = (IProcess) ac.getBean("process");
Process.doActions(process);

